Toyota Corolla (E120) 2002–2008 Repair Manual / Diagnostics / Sfi system / Engine coolant temperature circuit / Circuit description
Toyota Corolla (E120): Circuit description
A thermistor is built in the engine coolant temperature sensor and changes the resistance value according to the engine coolant temperature.
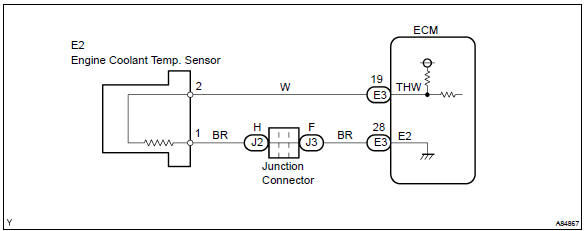
The structure of the sensor and connection to the ecm is the same as those of the intake air temperature sensor.
Hint
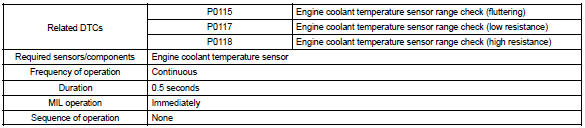
: if the ecm detects the dtc p0115, p0117 or p0118, it operates the fail–safe function in which the engine coolant temperature is assumed to be 80 c (176 °F).
|
Dtc no. |
Proceed to |
Dtc detection condition |
Trouble area |
| P0115 | Step 1 | Open or short in engine coolant temperature sensor circuit for 0.5 Seconds |
|
| P0117 | Step 4 | Short in engine coolant temperature sensor circuit for 0.5 Seconds | |
| P0118 | Step 2 | Open in engine coolant temperature sensor circuit for 0.5 Seconds |
Hint
: after confirming dtc p0115, p0117 or p0118, confirm the engine coolant temperature in the ”diagnosis/ enhanced obd ii/data list/all” using the hand–held tester or the obd ii scan tool.
Monitor description
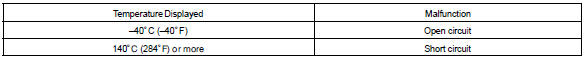
The engine coolant temperature (ect) sensor is used to monitor the engine coolant temperature. The ect sensor has a thermistor that varies its resistance depending on the temperature of the engine coolant. When the coolant temperature is low, the resistance in the thermistor increases. When the temperature is high, the resistance drops. The variations in resistance are reflected in the voltage output from the sensor. The ecm monitors the sensor voltage and uses this value to calculate the engine coolant temperature. When the sensor output voltage deviates from the normal operating range, the ecm interprets this as a fault in the ect sensor and sets a dtc.
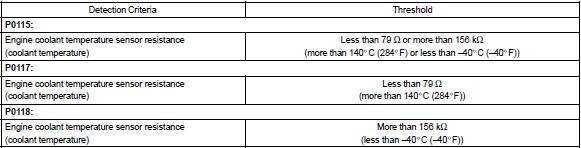
Example: when the ecm calculates that the ect is –40 c (–40 °F), or more than 140 c (284 °F), and if either the condition continues for 0.5 Sec or more, the ecm will set a dtc.
Monitor strategy
Typical enabling conditions

Typical malfunction thresholds
Component operating range

Wiring diagram
Other materials:
Dialing from the contacts list
You can dial a number from the contact data imported from your cellular phone.
The system has one contact for each registered phone. Up to 2500 contacts may be
stored in each contact. 1 Display the phone screen.
2 Select “Contacts” tab.
3 Choose the desired contact to call from the list.
...
Inspection procedure
1 Check side air bag sensor assy rh
Sst 09843–18040
Connect the negative (–) terminal cable to the battery,
and wait at least for 2 seconds.
turn the ignition switch to on, and wait at least for 20 seconds.
clear the dtc stored in memory .
turn the ignition swi ...
Inspection procedure
Hint:
read freeze frame data using the hand-held tester or the obd ii scan tool.
Freeze frame data records the
engine conditions when a malfunction is detected. When troubleshooting, it is
useful for determining whether
the vehicle was running or stopped, the engine was warmed up or not, the ...