Toyota Corolla (E120) 2002–2008 Repair Manual / Diagnostics / Sfi system / Catalyst system efficiency below
threshold / Circuit description
Toyota Corolla (E120): Circuit description
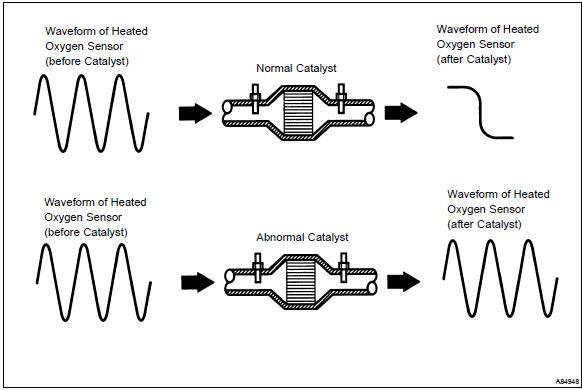
The ecm compares the two waveforms of the heated oxygen sensors located before and after the catalyst to determine whether or not the catalyst performance has deteriorated.
Air–fuel ratio feedback compensation keeps the waveform of the heated oxygen sensor in front of the catalyst alternates between back and forth, from rich to lean.
If the catalyst is functioning normally, the waveform of the heated oxygen sensor behind the catalyst switches back and forth between rich and lean much more slowly than the waveform of the heated oxygen sensor in front of the catalyst.
When both waveforms change at a similar rate, it indicates that the catalyst performance has deteriorated.
Monitor description
The vehicle is equipped with the two oxygen sensors (o2s). One is mounted upstream from the three–way catalytic (twc) converter (front heated oxygen sensor ”sensor 1” ), the second is mounted downstream (heated oxygen sensor ”sensor 2” ). The catalyst efficiency monitor compares the sensor 1 and 2 signals in order to calculate twc ability to store oxygen.
During normal operation, the twc stores and releases oxygen as needed. This results in low oxygen variations in the post twc exhaust stream as shown.
As the twc’s efficiency degrades, its ability to store oxygen is reduced. This causes higher variations in post twc exhaust stream oxygen content and results in increased sensor 2 signal activity as shown.
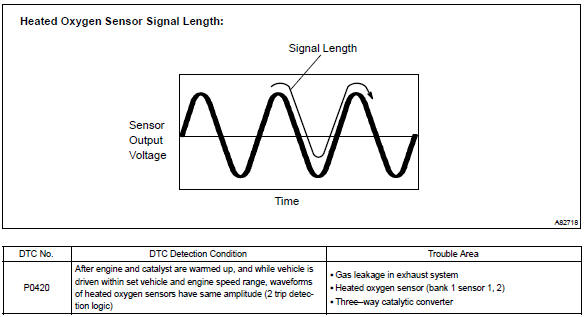
When running the monitor, the ecm compares sensor1 and sensor 2 signals over a specific time to determine the twc efficiency. The ecm begins by calculating the signal length for both sensors.
Monitor strategy
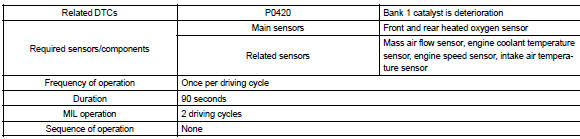
Typical enabling conditions
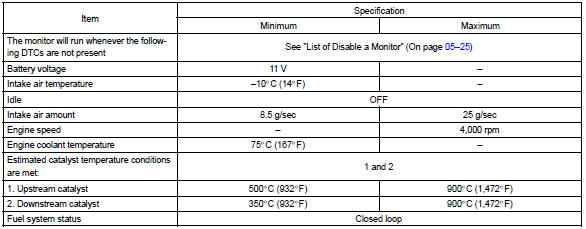
Typical malfunction thresholds

Component operating range

Monitor result (mode 06 data)

Refer for detailed information on checking monitor status.
Confirmation driving pattern
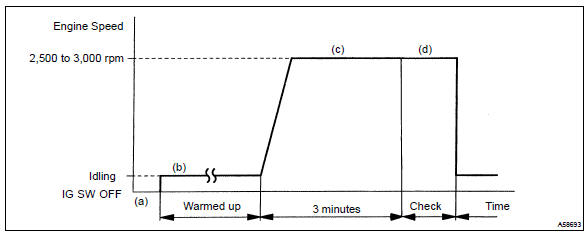
- Connect the hand–held tester to the dlc3, or connect the probe of the oscilloscope between terminals ox1a, ox1b and e1 of the ecm connector.
- start the engine and warm it up with all the accessories switched off until the engine coolant temperature becomes stable.
- run the engine at 2,500 to 3,000 rpm for about 3 minutes.
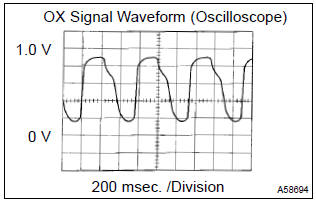
- after confirming that the waveform of the bank 1 sensor 1 (ox) which oscillates between 0 v and 1 v under a feedback to the ecm, check the waveform of the bank 1 sensor 2 (ox).
Hint
: if there is malfunction in the system, the waveform of ”sensor 2” (oxl2) may become a similar to the one of ”sensor1” (oxl1) shown in the diagram on the left.
Other materials:
Turning on the high beam headlights
1 With the headlights on, push the lever away from you to turn on the high beams.
Pull the lever toward you to the center position to turn the high beams off.
2 Pull the lever toward you and release it to flash the high beams once.
You can flash the high beams with the headlights on or off.
&# ...
Dtc check/clear
1. Dtc check (normal mode)
Notice:
hand–held tester only:
when the diagnostic system is switched from the normal
mode to the check mode, all the dtcs and freeze frame
data recorded in the normal mode will be erased. So before
switching modes, always check the dtcs and freeze frame
data, and ...
On–vehicle inspection
1. Check battery electrolyte level
Check the electrolyte quantity of each cell (maintenance–free battery).
If under the lower level, replace the battery (or add distilled
water if possible) and check the charging
system.
check the electrolyte quantity of each cell ...