Toyota Corolla (E120) 2002–2008 Repair Manual / Diagnostics / Sfi system / Random/multiple cylinder misfire
detected / Circuit description
Toyota Corolla (E120): Circuit description
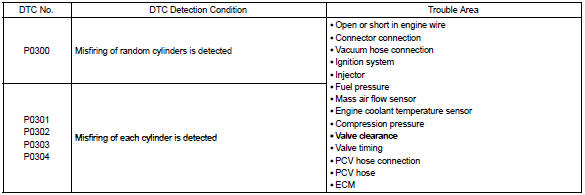
When a misfire occurs in the engine, hydrocarbons (hc) enter the exhaust in high concentrations. If this hc concentration is high enough, there could be an increase in exhaust emissions levels. High concentrations of hc passing through the catalyst also cause to temperature of the catalyst to increase, possibly damaging the catalyst. To prevent this increase in the emissions and limit the possibility of thermal damage, the ecm monitors the misfire rate. When the temperature of the catalyst reaches a point of thermal degradation, the ecm will blink the mil. For monitoring misfire, the ecm uses both the camshaft position sensor and crankshaft position sensor. The camshaft position sensor is used to identify misfiring cylinders and the crankshaft position sensor is used to measure variations in the crankshaft rotation speed. The misfire counter increments when crankshaft rotation speed variations exceed threshold values.
The ecm illuminates the mil if the misfiring rate exceeds a threshold value and could cause emissions deterioration.
Hint
: when codes for a misfiring cylinder are recorded repeatedly but no random misfire code is recorded, it indicates that the misfires have been detected and recorded at different times.
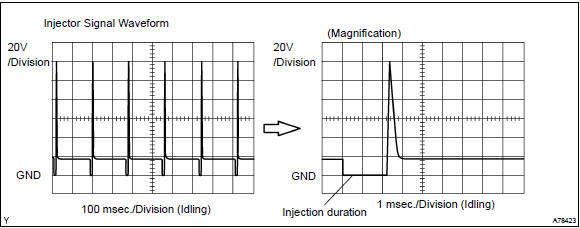
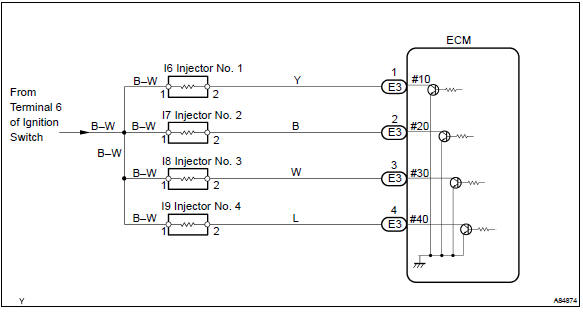
Reference: inspection using oscilloscope with the engine idling, check the waveform between terminals #10 to #40 and e01 of the ecm connectors.
Hint
: the correct waveform is as shown.
Monitor description

The ecm illuminates the mil if the misfiring rate exceeds a threshold value and could cause emissions deterioration.
The ecm will illuminate the mil when the percent misfire exceeds the specified limit per 1,000 engine revolutions.
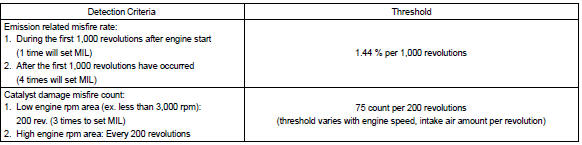
One occurrence of excessive misfire during engine start will set the mil. Four occurrences are required to set the mil 1,000 revolutions after engine start. (2 Trip detection logic) the mil blinks when ”percent misfire causing catalyst damage” per 200 revolution met 3 times (1 time if the engine rpm is in high speed range). (Mil blinks immediately)
Monitor strategy
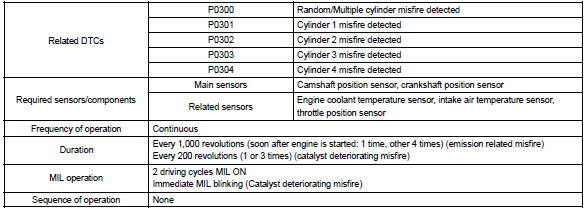
Typical enabling conditions
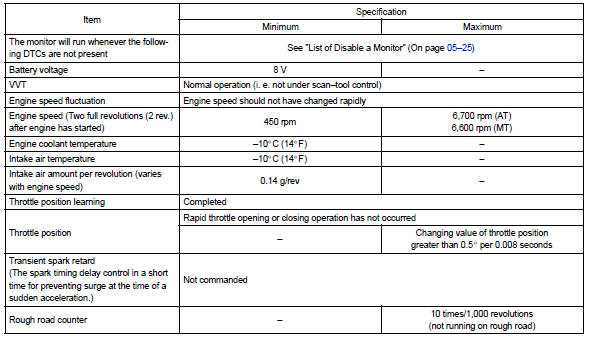
Typical malfunction thresholds
Wiring diagram
Refer to dtc p0351 for the wiring diagram of the ignition system.
Other materials:
Inspection procedure
1 Check d squib circuit(airbag sensor assy center – horn button
assy)
Disconnect the negative (–) terminal cable from the battery,
and wait at least for 90 seconds.
disconnect the connectors between the horn button assy
and the airbag sensor assy center.
for the oran ...
Inspection procedure
1 Inspect shift solenoid valve(sl)
Remove the shift solenoid valve sl.
measure the resistance according to the value(s) in the
table below.
Standard:
Connect the positive (+) battery lead to the solenoid connector
terminal, and the negative (–) battery lead to the
so ...
Riding with children
Observe the following precautions
when children are
in the vehicle.
Use a child restraint system
appropriate for the child,
until the child becomes
large enough to properly
wear the vehicle's seat belt.
It is recommended that children
sit in the rear seats to
avoid accidental contact
with the ...