Toyota Corolla (E120) 2002–2008 Repair Manual / Diagnostics / Sfi system / Engine coolant temp. Circuit
range/performance problem / Circuit description
Toyota Corolla (E120): Circuit description
Refer to dtc p0115
|
Dtc no. |
Dtc detection condition | Trouble area |
| P0116 | If engine coolant temperature (ect) was between 35 c (95 °F)
and 60 c (140 °F) when starting the engine, and also conditions
(a) and (b) are met:
|
|
If engine coolant temperature (ect) was more than 60 c
when starting the engine, and also conditions (a) and (b) are
met:
|
Monitor description
The engine coolant temperature (ect) sensor is used to monitor the engine coolant temperature. The ect sensor has a thermistor that varies its resistance depending on the temperature of the engine coolant. When the coolant temperature is low, the resistance in the thermistor increases. When the temperature is high, the resistance drops. The variations in resistance are reflected in the voltage output from the sensor. The ecm monitors the sensor voltage and uses this value to calculate the engine coolant temperature. When the sensor output voltage deviates from the normal operating range, the ecm interprets this as a fault in the ect sensor and sets a dtc.
Examples:
- upon starting the engine, the coolant temperature (ect) was
between 35 c (95 °F) and 60 c (140 °F).
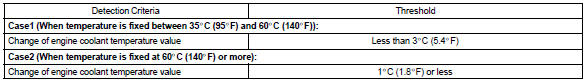
If after driving for 250 seconds, the ect still remains within 3 c (5.4 °F) of the staring temperature, a dtc will be set. (2 Trip detection logic)
- upon starting the engine, the coolant temperature (ect) was over 60 c (140 °F). If after driving for 250 seconds, the ect still remains within 1 c (1.8 °F) of the starting temperature, a dtc will be set. (6 Trip detection logic)
Monitor strategy
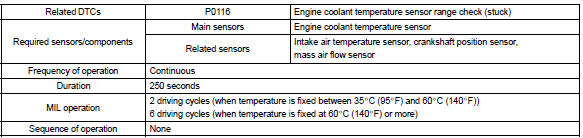
Typical enabling conditions
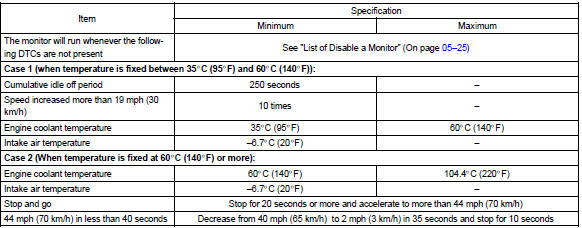
Typical malfunction thresholds
Component operating range

Wiring diagram
Refer to dtc p0115
Other materials:
Rear axle beam assy
Replacement
Hint: components:
1. Remove rear wheel
remove the rh and lh rear wheels.
2. Remove rear brake drum sub–assy
3. Separate skid control sensor wire
Disconnect the skid control sensor connector.
remove the 2 bolts and separate the wire harness
clamp ...
Communication system
Horn system
Location
Problem symptoms table
Inspection
1. Inspect low pitched horn assy
Connect the positive (+) lead from the battery to the terminal
and the negative (–) lead to the horn body, and check
that the horn blows.
If the result is not as specified, replace the ...
Warning lights
Warning lights inform the driver of malfunctions in the indicated vehicle’s systems.
*1: Vehicles without a smart key system:
These lights turn on when the engine switch is turned to the “ON” position to indicate
that a system check is being performed. They will turn off after the engi ...