Toyota Corolla (E120) 2002–2008 Repair Manual / Diagnostics / Sfi system / Intake air temperature circuit / Circuit description
Toyota Corolla (E120): Circuit description
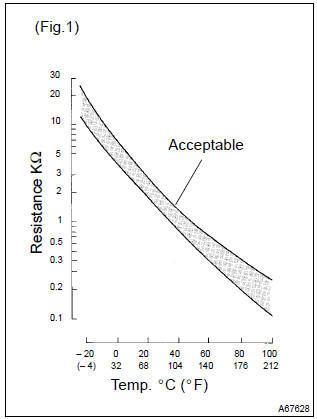
The intake air temperature (iat) sensor, mounted on the mass air flow (maf) sensor, monitors the intake air temperature. The iat sensor has a thermistor that varies its resistance depending on the temperature of the intake air. When the air temperature is low, the resistance in the thermistor increases. When the temperature is high, the resistance drops. The variations in resistance are reflected as voltage changes to the ecm terminal.
(See fig. 1).
The intake air temperature sensor is connected to the ecm.
The 5 v power source voltage in the ecm is applied to the intake air temperature sensor from terminal tha (thar) via resistor r.
That is, the resistor r and the intake air temperature sensor are connected in series. When the resistance value of the intake air temperature sensor changes in accordance with changes in the intake air temperature, the potential at terminal tha (thar) also changes. Based on this signal, the ecm increases the fuel injection volume to improve the drive ability during cold engine operation.
|
Dtc no. |
Proceed to |
Dtc detection condition |
Trouble area |
| P0110 | Step 1 | Open or short in intake air temperature sensor circuit for 0.5 Seconds |
|
| P0112 | Step 4 | Short in intake air temperature sensor circuit for 0.5 Seconds | |
| P0113 | Step 2 | Open in intake air temperature sensor circuit for 0.5 Seconds |
Hint
: after confirming dtc p0110, p0112 or p0113, confirm the intake air temperature in the ”diagnosis / enhanced obd ii / data list / all” using the hand–held tester or the obd ii scan tool.
Monitor description
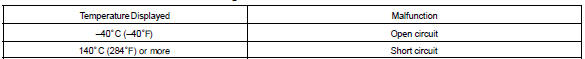
The ecm monitors the sensor voltage and uses this value to calculate the intake air temperature. When the sensor output voltage deviates from the normal operating range, the ecm interprets this as a fault in the iat sensor and sets a dtc.
Example: when the sensor voltage output equal to –40 c (–40 °F) or more than 140 c (284 °F).
Monitor strategy
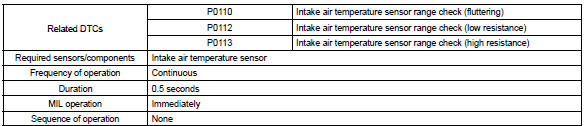
Typical enabling conditions

Typical malfunction thresholds
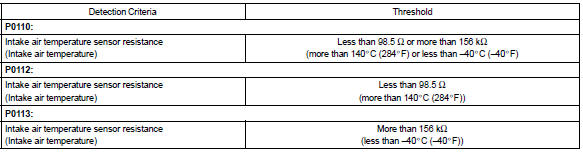
Component operating range

Wiring diagram
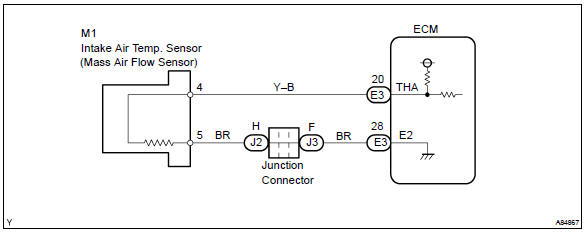
Other materials:
Luggage compartment door garnish outside
Replacement
Hint:
the installation procedures are the removal procedures in reverse order.
However, only installation procedures
requiring additional information are included.
1. Remove luggage compartment lock cylinder & key set
remove the 2 nuts and luggage compartment lock cyl ...
Circuit description
Monitor description
The ecm commands gearshift by turning the shift solenoid valves ”on/off”.
When there is an open or short
circuit in any shift solenoid valve circuit, the ecm detects the problem and the
mil comes on. Illuminating
the mil, the ecm performs the fail–safe and turns ...
Audio system types
► Without Multimedia system
► With Multimedia system
► With navigation system
Owners of models equipped with a navigation system should refer to the “Navigation
System Owner's Manual”.
■Using cellular phones
Interference may be heard through the audio system ...