Toyota Corolla (E120) 2002–2008 Repair Manual / Introduction / How to troubleshoot ecu controlled
systems / Symptom confirmation and diagnostic trouble code
Toyota Corolla (E120): Symptom confirmation and diagnostic trouble code
Hint
:
- the diagnostic system in corolla has various functions. The first function is the diagnostic trouble code (dtc) check, in which a malfunction in the signal circuits to the ecu is stored in code form in the ecu memory. Another function is the input signal check, which checks if the signals from various switches are sent to the ecu correctly. By using these check functions, it is possible to quickly narrow down potential problem areas and troubleshooting can be performed effectively. The diagnostic functions are incorporated in the following systems in the corolla.
|
System |
Diagnostic trouble code check | Input signal check (sensor check) | Diagnostic test mode (active test) |
| Sfi system | 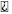 (With check mode) |
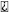 |
 |
| Abs with ebd system |  |
 |
|
| Electronic controlled automatic transaxle [ect] |  (With check mode) |
 |
|
| Supplemental restraint system |  |
||
| Cruise control system |  |
- In the dtc check, it is very important to determine whether the problem indicated by the dtc is still occurring or has occurred in the past but returned to normal at present. In addition during the problem symptom check, it a check must be made on whether the malfunction indicated by the dtc is directly related to the problem symptom or not. For this reason, the dtc should be checked before and after symptom confirmation to determine the current conditions. If this is not done, it may, depending on the case, result in unnecessary troubleshooting for systems that are operating normally. This would make more difficult to detect the problem area or to try to repair irrelevant areas. Therefore, always follow the procedures in the correct order and perform the dtc check.
- A flow chart showing how to proceed with troubleshooting using the diagnostic trouble code (dtc) check is shown the this page. This flow chart shows how to utilize the dtc check effectively. Then, by carefully checking the results, this chart indicates how to proceed either to the dtc troubleshooting or to the troubleshooting of the problem symptoms table.
1 Dtc check
2 Making a note and clear the dtcs
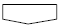
3 Symptom confirmation
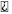 |
Problem symptoms exist |
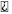 |
No problem symptoms exist |
A go to step 5
B
4 Simulation test using the symptom simulation methods
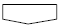
5 Dtc check
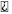 |
Dtc displayed |
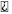 |
Normal code displayed |
A troubleshooting of problem indicated by dtc
B
6 Symptom confirmation
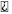 |
No problem symptoms exist |
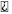 |
Problem symptoms exist |
If a dtc is displayed in the initial dtc check, it indicates that a trouble may have occurred in a wire harness or connector in that circuit in the past, therefore check the wire harness and connectors .
A system normal
B
Troubleshooting of each problem symptom
The problem is still occurring in a place other than the diagnostic circuit (the dtc displayed first is either for a past problem or it is a secondary problem).
Other materials:
Replacement
1. Remove console box sub–assy rear
2. Remove parking brake lever sub–assy
Disconnect the parking brake switch connector from the
parking brake switch.
remove the lock nut and adjusting nut from the parking
brake cable assy no.1.
Remove the 2 bolts.
Usin ...
Inspection procedure
Hint:
hand–held tester only:
narrowing down the trouble area is possible by performing ”a/f control” active
test (heated oxygen
sensor or other trouble areas can be distinguished).
Perform active test using hand–held tester (a/f control).
Hint:
”a/f control” is the active te ...
Foamed material application areas
If an increase in temperature or other condition damages the foamed material
when repairing or replacing the panel,
fill in the insufficient areas with urethane foam. The following illustration
shows the areas for one side, but the
foamed material must be applied equally to both the left and r ...