Toyota Corolla (E120) 2002–2008 Repair Manual / Diagnostics / Sfi system / Oxygen sensor heater control
circuit... / Circuit description
Toyota Corolla (E120): Circuit description
Refer to dtc p0130
Hint
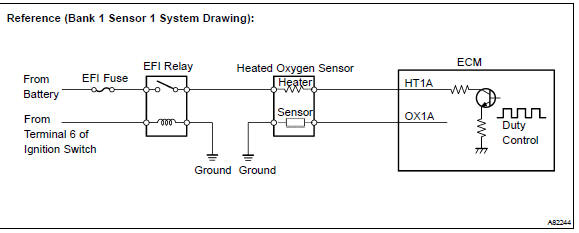
: the ecm provides a pulse width modulated control circuit to adjust current through the heater. The heated oxygen sensor heater circuit uses a relay on the b+ side of the circuit.
Monitor description
The ecm uses the heated oxygen sensor information to regulate the air–fuel ratio close to a stoichiometric ratio. This maximizes the catalytic converter’s ability to purify the exhaust gas. The sensor detects oxygen levels in the exhaust gas and sends this signal to the ecm.
The inner surface of the sensor element is exposed to the outside air. The outer surface of the sensor element is exposed to the exhaust gas. The sensor element is made of the platinum coated zirconia and includes an integrated heating element. The heated oxygen sensor has the characteristic whereby its output voltage change suddenly in the vicinity of the stoichiometric air–fuel ratio. When heated, the sensor becomes very efficient. If the temperature of the exhaust is low, the sensor will not generate useful voltage signals without supplemental heating. The ecm regulates the supplemental heating using a duty–cycle approach to regulate the average current in the heater element. If the heater current is out of the normal range, the sensor’s output signals will be inaccurate and the ecm cannot regulate the air–fuel ratio properly. When the heater current is out of the normal operating range, the ecm interprets this as a malfunction and sets a dtc.
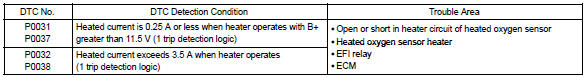
Example: the ecm will set a high current dtc if the current in the sensor is more than 2 a when the heater is off.
Similarly, the ecm will set a low current dtc if the current is less than 0.25 A when the heater is on.
Monitor strategy
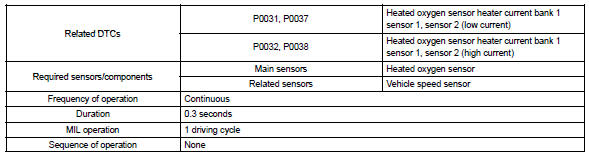
Typical enabling conditions
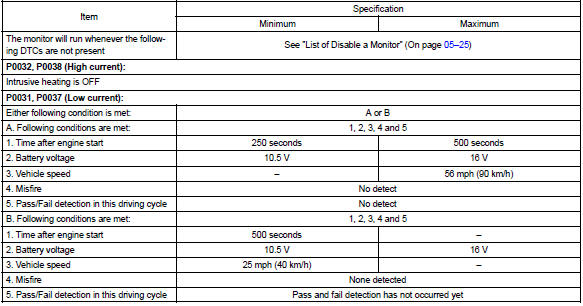
Typical malfunction thresholds
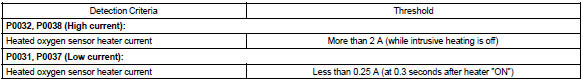
Component operating range
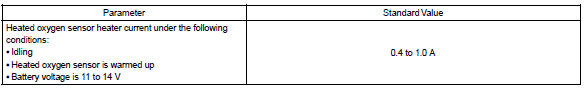
Monitor result (mode 06 data)
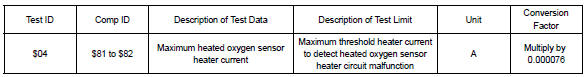
Refer to page 05–27 for detailed information on checking monitor status.
Wiring diagram
Refer to dtc p0130
Other materials:
Transmitter battery
Replacement
1. Replace transmitter battery
Notice:
special caution should be taken for handling each component as they are
precision electronic components.
Using a screwdriver, pry out the transmitter case.
Notice:
do not forcibly pry out the case.
Hint:
tape the screwdriver tip ...
Engine (ignition) switch (vehicles
without a smart key system)
Starting the engine
1. Check that the parking brake
is set.
2. Check that the shift lever is in
P.
3. Firmly depress the brake
pedal.
4. Turn the engine switch to
START to start the engine.
■If the engine does not start
The engine immobilizer system may
not have been deactivated.
Contact your Toy ...
Vehicle control system
Ignition or starter switch assy
Replacement
1. Remove steering column cover
2. Remove ignition or starter switch assy
Disconnect the ignition switch connector and unlock
warning switch connector.
remove the 2 clamps.
remove the 2 screws and ignition switch.
Inspectio ...