Toyota Corolla (E120) 2002–2008 Repair Manual / Diagnostics / Sfi system / Mass or volume air flow circuit
range/performance problem / Circuit description
Toyota Corolla (E120): Circuit description
Refer to dtcs p0100
|
Dtc no. |
Dtc detection condition | Trouble area |
| P0101 | After engine is warmed up, conditions (a) to (d) continue for
more than 10 seconds (2 trip detection logic):
|
|
Conditions (a) and (b) continue for more than 6 seconds: (2 trip
detection logic)
|
Monitor description
The maf (mass air flow) sensor helps the ecm calculates the amount of air flowing through the throttle valve. The ecm uses this information to determine the fuel injection time and provides a proper air–fuel ratio.
Inside the maf sensor, there is a heated platinum wire exposed to the flow of intake air. By applying a specific current to the wire, the ecm heats this wire to a given temperature. The flow of incoming air cools the wire and an internal thermister, changing their resistance. To maintain a constant current value, the ecm varies the voltage applied to these components in the maf sensor. The voltage level is proportional to the air flow through the sensor and the ecm interprets this voltage as the intake air amount. If there is a defect in the sensor or an open or short circuit, the voltage level will deviate outside the normal operating range. The ecm interprets this deviation as a defect in the maf sensor and sets a dtc.
Example: if the voltage is more than 2.2 V at idle, or less than 0.4 V at idle off, the ecm interprets this as a defect in the maf sensor and sets a dtc.
Monitor strategy

Typical enabling conditions
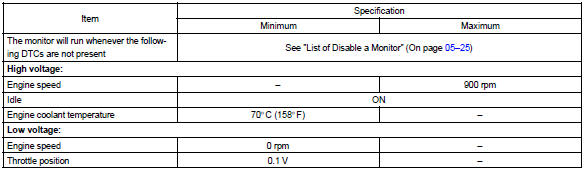
Typical malfunction thresholds

Wiring diagram
Refer to dtc p0100
Other materials:
Odometer and trip meter
display
■ Changing the display
Press the display change button
until the desired item is displayed.
■ Display items
Odometer
Displays the total distance the vehicle
has been driven.
Trip meter A/Trip meter B
Displays the distance the vehicle
has been driven since the meter
was last reset. Trip me ...
Inspection procedure
1 Input signal check
See input signal check on page 05–745.
check the indicator light operation when each of the set/
coast, resume/accel and cancel is turned on.
Ok:
set/coast, resume/accel switch:
the signals shown in the table on the left should be
output when each switch is ...
Safety information for
Safety Connect
Important! Read this information
before using Safety Connect.
■ Exposure to radio frequency
signals
The Safety Connect system
installed in your vehicle is a
low-power radio transmitter and
receiver. It receives and also
sends out radio frequency (RF)
signals.
In August 1996, the Federal
Communica ...